| |
IF THEN ELSE statement
IF THEN ELSE END-IF statement
Format
IF condition-1 THEN
Statements-1
..
[ELSE statements-2 .. ]
[END-IF].
- condition-1 is any of the conditions discussed in previoius pages
- Statements-1 OR Statements-2 contains one or more COBOL statements
- END-IF is the scope terminator. IF statement ends with this scope terminator
Note : Instead of END-IF, we can use period as scope terminator.
Structured programming rules recommends to use END-IF rather than period (.)
- using THEN keyword is optional
condition associated with IF statement , becomes true then all statements represented
by Statements-1 are get executed. Condition associated with IF statement , becomes
false then all statements represented by Statements-2 are get executed.
Below picture represents what we discussed.
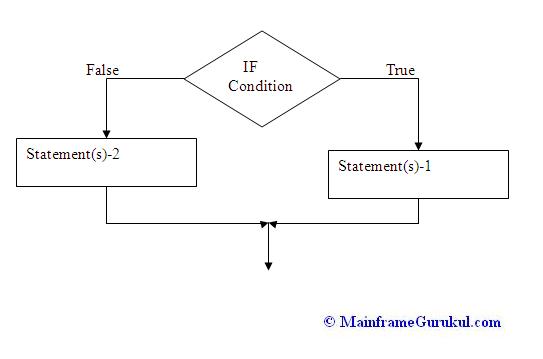 Example. IF WS-A > ZERO AND WS-B > ZERO THEN
COMPUTE POSITIVE-AMT = WS-A + WS-B
END-IF
In the above example, COMPUTE statement execute only when the condition associated with
IF statement becomes true. i.e., WS-A & WS-B should contains positive values.
Example 2. IF WS-A > ZER0 AND WS-B > ZERO THEN
COMPUTE POSITIVE-AMT = WS-A + WS-B
ELSE
DISPLAY ' One of the input amount are not positive '
DISPLAY 'WS-A value ', WS-A
DISPLAY 'WS-B value ', WS-B
END-IF.
In this example, we have use ELSE keyword. If the condition associated with IF statement
is true then the COMPUTE statement will get executed. If the condition is false, the
statements after ELSE keyword will get executed.
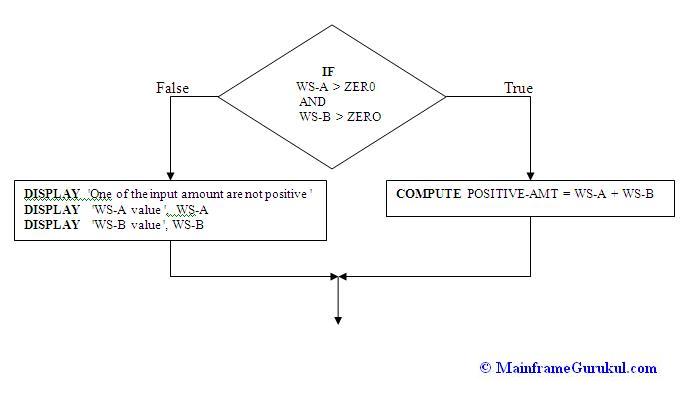
Below picture represents what we discussed above.
Example. IF WS-A > ZERO AND WS-B > ZERO THEN
COMPUTE POSITIVE-AMT = WS-A + WS-B
END-IF
In the above example, COMPUTE statement execute only when the condition associated with
IF statement becomes true. i.e., WS-A & WS-B should contains positive values.
Example 2. IF WS-A > ZER0 AND WS-B > ZERO THEN
COMPUTE POSITIVE-AMT = WS-A + WS-B
ELSE
DISPLAY ' One of the input amount are not positive '
DISPLAY 'WS-A value ', WS-A
DISPLAY 'WS-B value ', WS-B
END-IF.
In this example, we have use ELSE keyword. If the condition associated with IF statement
is true then the COMPUTE statement will get executed. If the condition is false, the
statements after ELSE keyword will get executed.
Below picture represents what we discussed above.
 NEXT SENTENCE
NEXT SENTENCE can be used in the place of either Statements-1 (THEN part) or Statements-2
(ELSE part) in IF statement.
- if there is no action required either in THEN part OR ELSE part of IF statement we can
use this NEXT SENTENCE
- It will transfer control to next statement after the nearest period
- Please make note that control wont pass to the next statement of END-IF, in this case.
NEXT SENTENCE only check for closest period and execute the statements after that.
Example -
MOVE 100 TO WS-A.
MOVE 200 TO WS-B.
MOVE 300 TO WS-C.
IF WS-A > ZER0 AND WS-B > ZERO THEN
NEXT SENTENCE
ELSE
DISPLAY ' One of the input amount are not positive '
DISPLAY 'WS-A value ', WS-A
DISPLAY 'WS-B value ', WS-B
END-IF
ADD WS-A TO WS-C.
DISPLAY 'WS-C value', WS-C.
Simple Test - Tell me what value will be displayed for the WS-C (last display statement
in the above example) ?
Ans : 300
OK, let me explain, why the above example displayed 300 instead of 400.
If you observe there is no period after END-IF, period is there after ADD statement.
Since the condition associated with IF statement is true, NEXT SENTENCE tranfered the
control to the statement after closest following period, then DISPLAY statement
displayed the WS-C value ADD statement did not get executed.
Below picture shows the same what we discussed till now.
NEXT SENTENCE
NEXT SENTENCE can be used in the place of either Statements-1 (THEN part) or Statements-2
(ELSE part) in IF statement.
- if there is no action required either in THEN part OR ELSE part of IF statement we can
use this NEXT SENTENCE
- It will transfer control to next statement after the nearest period
- Please make note that control wont pass to the next statement of END-IF, in this case.
NEXT SENTENCE only check for closest period and execute the statements after that.
Example -
MOVE 100 TO WS-A.
MOVE 200 TO WS-B.
MOVE 300 TO WS-C.
IF WS-A > ZER0 AND WS-B > ZERO THEN
NEXT SENTENCE
ELSE
DISPLAY ' One of the input amount are not positive '
DISPLAY 'WS-A value ', WS-A
DISPLAY 'WS-B value ', WS-B
END-IF
ADD WS-A TO WS-C.
DISPLAY 'WS-C value', WS-C.
Simple Test - Tell me what value will be displayed for the WS-C (last display statement
in the above example) ?
Ans : 300
OK, let me explain, why the above example displayed 300 instead of 400.
If you observe there is no period after END-IF, period is there after ADD statement.
Since the condition associated with IF statement is true, NEXT SENTENCE tranfered the
control to the statement after closest following period, then DISPLAY statement
displayed the WS-C value ADD statement did not get executed.
Below picture shows the same what we discussed till now.
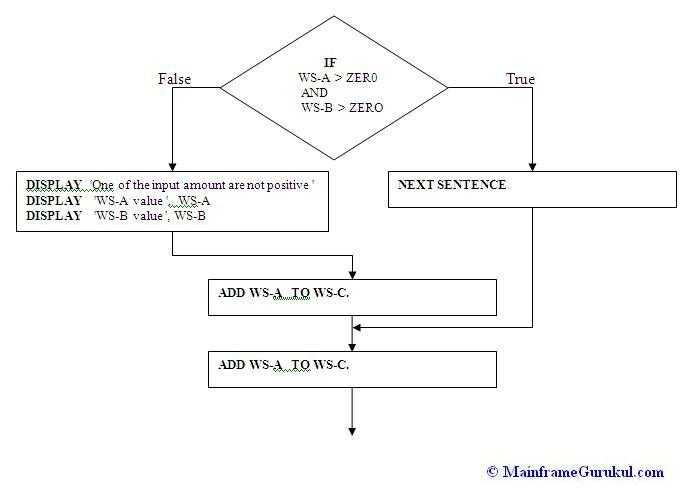 If you have a period after END-IF, WS-C value will be 400. because ADD statement will
get executed in this case. Quite interesting, isn't it?
Normally we may face the interview question on differences between CONTINUE (cobol 85)
and NEXT SENTENCE (cobol 74). CONTINUE is dummy statement, control will continue as if
there are no statements, i.e., it wont do any control transfers. In above example, if
you have CONTINUE statement instead of NEXT SENTENCE , o/p will be 400.
Nested IF statements
One IF statement can contain one or more IF statements within it.
As shown below.
IF condition-1
IF condition-2
Statements-1
ELSE
Statements-2
END-IF
ELSE
IF condition-3
Statements-3
ELSE
Statements-4
END-IF
END-IF
- In nested IF conditions, each END-IF paired with the preceding IF.
- It is suggested to use END-IF as scope terminator instead of period
- In COBOL 74 we dont have END-IF scope terminator, need to use ELSE NEXT SENTENCE as
and when required for proper pairing of ELSE part with IF statement. ( In COBOL 85
we have END-IF, so it is suggested not to use period as scope terminator in nested
IF conditions for better readability and to reduce errors )
If you have a period after END-IF, WS-C value will be 400. because ADD statement will
get executed in this case. Quite interesting, isn't it?
Normally we may face the interview question on differences between CONTINUE (cobol 85)
and NEXT SENTENCE (cobol 74). CONTINUE is dummy statement, control will continue as if
there are no statements, i.e., it wont do any control transfers. In above example, if
you have CONTINUE statement instead of NEXT SENTENCE , o/p will be 400.
Nested IF statements
One IF statement can contain one or more IF statements within it.
As shown below.
IF condition-1
IF condition-2
Statements-1
ELSE
Statements-2
END-IF
ELSE
IF condition-3
Statements-3
ELSE
Statements-4
END-IF
END-IF
- In nested IF conditions, each END-IF paired with the preceding IF.
- It is suggested to use END-IF as scope terminator instead of period
- In COBOL 74 we dont have END-IF scope terminator, need to use ELSE NEXT SENTENCE as
and when required for proper pairing of ELSE part with IF statement. ( In COBOL 85
we have END-IF, so it is suggested not to use period as scope terminator in nested
IF conditions for better readability and to reduce errors )
|
|



